Today, the Internet of Things has become an inseparable part of human life. The energy consumption of these devices is often supplied from an energy source such as batteries or in the form of energy extraction from the surrounding and external environment, so it is necessary to reduce the power consumption. The problem we are considering is reducing the energy consumption of memory because a large part of the energy of the Internet of Things device is consumed by the memory, which is continuously storing programs and data and performing activities of this kind.
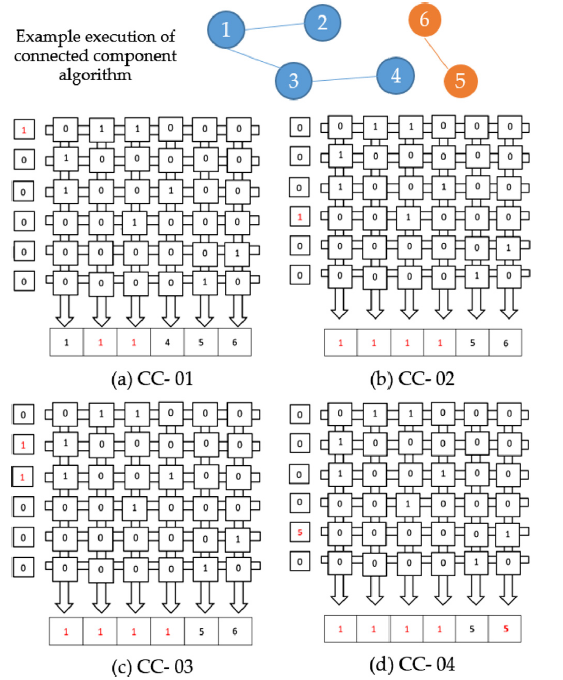
In this research, it is tried to map the data in the memory with two different levels, in the form of Runtime and according to their behavior to each of the appropriate levels. To achieve this goal, we need the access bit to detect the reference to a block, a table for remapping and a controller to periodically check the access bit, in order to take into account the importance of the percentage of write operations in a level with low STT-MRAM memory retention and a With its high retention level, we can reduce energy consumption. The issue that has become a problem in STT-MRAM memory in relation to energy is the high writing energy of this memory. As a result of the research in the field of reducing the energy consumption of STT-MRAM, it is very important. Treating different data read and write requests in the same way will result in wasted energy. It should be noted that in the application of the Internet of Things, the data show different behavior in terms of their retention time. Some of them are the type of work data that are written and read in short intervals, while others are read and written only once and in a long period of time. Finally, the results show that our proposed architecture has reduced the consumed energy by an average of 66% compared to the basic architecture.
Key Words: Embedded STT-MRAM, Low Power Memory, IOT Applications, Data Mapping
Latest Posts
-
Dec 06, 2024
-
Oct 25, 2024