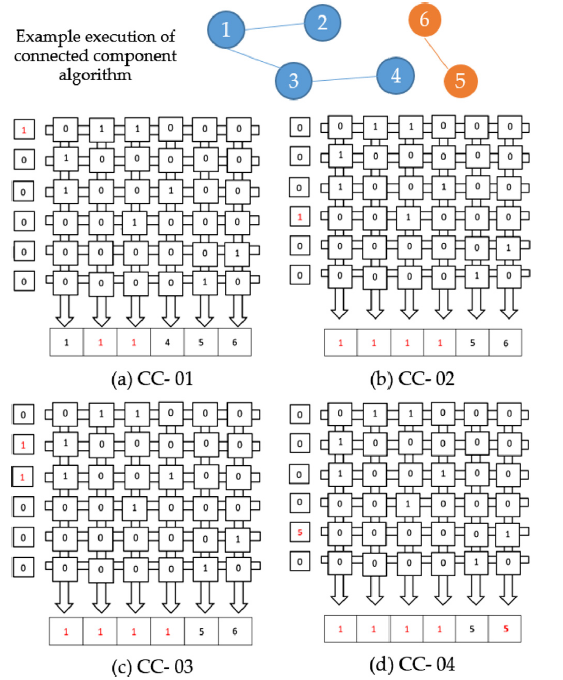
Memory in computer systems is considered a bottleneck for system speed because it responds slowly to processor requests. This is particularly noticeable and limiting when the system works with large datasets. Additionally, transferring data between memory and the processor for processing is very energy-intensive. Given the increasing use of large datasets and the need to process them, a novel approach called in-memory processing has been introduced in computer system architecture. This approach aims to reduce energy consumption and data transfer delays between memory and the processor. However, due to the novelty of this idea, this architecture faces many challenges. For example, to achieve energy efficiency, system performance may fall below optimal levels, or specific-purpose applications processed in these architectures may compete with the central processor for shared resources (such as big data), leading to interference and not achieving the expected improvements. In this research, an in-memory processing architecture for a large dataset sorting algorithm is presented with an approach to reduce energy consumption while maintaining system performance at an optimal level. Implementing this external sorting algorithm in the mentioned architecture results in a 57% reduction in energy consumption and a 2.9-fold acceleration in sorting operations compared to executing the same algorithm in traditional computer system architectures.
Keywords: In-memory processing, big data, external sorting, non-volatile memory.
Latest Posts
-
Oct 25, 2024
-
Oct 25, 2024